Projects Translational Immunology

Tissue inflammation upon chronic rheumatic diseases
Patients with chronic rheumatic diseases suffer from frequent and severe courses of infections. In particular, a high inflammatory burden increases the risk for secondary infections. Inflammatory responses can differ a lot within different tissues. The aim of this project is to characterize the tissue inflammation in different chronic rheumatic diseases to develop better treatment strategies against inflammation. Thus, not only autoimmunity but also the risk for resulting secondary infections can be reduced.
A specific focus is laid on the connective tissues disease systemic sclerosis. The pathophysiology of systemic sclerosis is still unclear. Affected patients suffer from severe inflammation of the skin and blood vessels, the lung, and the cardiac system. In close collaboration with the Hannover Medical School, immune cells from inflamed tissue of such patients are analyzed. This approach shall help to identify novel therapy objectives for patients with systemic sclerosis.
Funding
Hannover Biomedical Research School (HBRS) and the Centre for Infection Biology (ZIB); DFG-funded "International research training group" (IRTG) 1273; Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) Klinische Forschergruppe (KFO 250)
Indirect effects of immunomodulatory drugs
For the treatment of chronic rheumatic diseases, a whole bunch of immunomodulatory treatments is approved. Treatment strategies aim for blocking of cytokines, immune cell receptors or pathways, or even deplete complete immune cell subsets. Since immune responses are based on a close network and crosstalk between different cell types, the immunomodulatory treatment of one cell type can sustainably affect the overall immune response. In particular, upon vaccination responses and infections the mode of action of immunomodulatory drugs has to be clearly understood. This project aims to better characterize indirect effects of immunomodulatory drugs on vaccination responses to identify optimal drugs for patients to guarantee also optimal vaccination responses.
Funding
DFG, German Research Foundation grant SFB900; Germany's Excellence Strategy – EXC 2155 “RESIST”; Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) Klinische Forschergruppe (KFO 250)
Cell-selective targeting of immune cells
Systemic treatment with immunomodulatory drugs can lead to systemic side effects. Liposomal or synthetic nanocarriers are capable to deliver active substances directly into target cells. To address specific cell types, nanocarriers are functionalized to allow a cell-selective targeting. This project aims to test nanocarriers as target strategy for myeloid cells. Using cell-selective targeting approaches to conduct active agents into target cells, systemic side effects can be minimized while local effective dosages can be increased.
Funding:
German Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology (BMWi), via the Consortium of Industrial Research Associations (AiF), ZIM Program, Grant KF2531702AJ3; DFG, German Research Foundation grant SFB900; Germany's Excellence Strategy – EXC 2155 “RESIST”
Hirche C, Frenz T, Haas S, Döring M, Borst K, Tegtmeyer P, Brizic I, Jordan S, Keyser K, Chhatbar C, Pronk E, Lin S, Messerle M, Jonjic S, Falk CS, Trumpp S, Essers M, Kalinke U (2017) Systemic virus infections differentially modulate cell cycle state and functionality of long-term hematopoietic stem cells in vivo. Cell Rep 19(11): 2345-2356.
Borst K, Frenz T, Spanier J, Tegtmeyer PK, Chhatbar C, Skerra J, Ghita L, Namineni S, Lienenklaus S, Koster M, Heikenwaelder M, Sutter G, Kalinke U (2018) Type I interferon receptor signaling delays Kupffer cell replenishment during acute fulminant viral hepatitis. J Hepatol 68(4): 682-690.
Frenz T, Grabski E, Buschjager D, Vaas LA, Burgdorf N, Schmidt RE, Witte T, Kalinke U (2016) CD4+ T cells in patients with chronic inflammatory rheumatic disorders show distinct levels of exhaustion. J Allergy Clin Immunol 138(2): 586-589 e10.
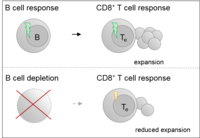
Graalmann T, Borst K, Manchanda H, Vaas L, Bruhn M, Graalmann L, Koster M, Verboom M, Hallensleben M, Guzman CA, Sutter G, Schmidt RE, Witte T, Kalinke U (2021) B cell depletion impairs vaccination-induced CD8(+) T cell responses in a type I interferon-dependent manner. Ann Rheum Dis (in press).
Frenz T, Grabski E, Buschjager D, Vaas LA, Burgdorf N, Schmidt RE, Witte T, Kalinke U (2016) CD4+ T cells in patients with chronic inflammatory rheumatic disorders show distinct levels of exhaustion. J Allergy Clin Immunol 138(2): 586-589 e10.
Duran V, Grabski E, Hozsa C, Becker J, Yasar H, Monteiro JT, Costa B, Koller N, Lueder Y, Wiegmann B, Brandes G, Kaever V, Lehr CM, Lepenies B, Tampe R, Forster R, Bosnjak B, Furch M, Graalmann T, Kalinke U (2021) Fucosylated lipid nanocarriers loaded with antibiotics efficiently inhibit mycobacterial propagation in human myeloid cells. J Control Release 334: 201-212.
Frenz T, Grabski E, Duran V, Hozsa C, Stepczynska A, Furch M, Gieseler RK, Kalinke U (2015) Antigen presenting cell-selective drug delivery by glycan-decorated nanocarriers. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 95(Pt A): 13-17.